What is work ability?
Work ability shows a person’s potential to cope with work demands at a given time. The development of individual functional capacity must be indicated in relation to these requirements. Both the worker and their job duties/claims may change over time and, where necessary, must be designed to be appropriate for the worker’s age, aging and health.

Where did it all begin?
Work ability concept
A globally well-known concept for such an integrated (holistic) approach is the work ability model. The instrument ‘Work Ability Index’ can be used to measure the degree of fit between individual capacity and work requirements. With further written or oral surveys, findings can be concretised and in workshops or other counselling settings, needs for change can be identified and appropriate measures to promote work ability can be determined.
Urgently needed are measures to ensure that working people:
have a job (employability)
are able to stay longer and well in work (work ability), and
are able, willing and allowed to carry out work productively and well (work well-being)
How to measure work ability?
Index of work ability as a tool for its measurement
Work ability can be measured. The work ability Index (WAI) is an internationally used survey instrument for the assessment of the current balance (stability and matching) between the work requirements and the individual capacities of a person. The resulting index number lies between 7 and 49 points; the higher the point value is, the more stable is the work ability.
The WAI is implemented in Finland as a standard instrument during first and repeated occupational health checks, e.g. by the Occupational Health Service. The validity and reliability of the WAI was tested.
WAI is a simple method that can be done online, but is usually used as a questionnaire in institutional proceedings, during which it must be completed by a self-assessed person.

Benefits of the work ability index
- it is a suitable tool in predicting the development of changes in work ability for different occupational groups;
- with the knowledge of the weak factors of work ability, it is possible to precisely target the support of the worker already at the initial stage of his problem;
- The work ability index can also be a useful tool in determining a worker’s risk of incapacity for work in the near future.
What is age management?
Pillars of age management
If we want to positively influence the management methods of the organization, it is appropriate that all procedures and methods that can positively affect its performance and prosperity are objectively identified, described, and newly introduced into practice.
The basic prerequisite for the effective implementation of specific and measurable age management actions in the practice of organizations is the evaluation of the fulfillment of individual pillars of age management, but also the objective knowledge of the results of measuring the work ability of employees.
Their overview, intended for an efficient evaluation of the initial state of age management, is given in the following points.ců.
The identification and quantification of all eight pillars and their fulfillment should form the basic input data for the creation of a strategy and the implementation of age management measures at the organizational level.
- Good knowledge of age structures.
- Positive attitudes towards aging.
- Good management that understands individuality and diversity.
- Well-functioning age strategy.
- Ensuring good work ability, motivation, and the will to continue working.
- High level of competencies.
- Good work and workplace organization.
- Good life.
Other age management tools
Personal radar
It is an innovative tool for individual assessment of employee´s work ability and well-being, which expands on the original WAI 1.0 by measuring other factors aimed at better understanding the employee’s work well-being, and thus a more comprehensive identification of reasons or obstacles regarding its optimization. The removal of these can lead to a strengthening of work ability. The outcomes will provide the employee a new picture of the level of their work ability and the reasons for their current condition. The management of the organization will obtain anonymous data about well-being of its employees, which will allow them to adjust the scope of measures applied in this area, which is the subject of the second part of the process called the Company Radar.
The Personal Radar questionnaire has 23 questions formulated in accordance with the content and factors of the work ability house. It includes 5 factors determining the work well-being of the and as a sixth factor there are six questions determining his work ability.
Company radar
What is work ability house?
A person’s employment in connection with experiencing a longer worklife relies on good health in particular, but other factors that influence this ability are just as important. However, the ability to learn and thus adapt to environmental changes and competence requirements is playing an increasingly important role, as are our values, attitudes and motivations to work. Satisfaction with our work and conditions at the workplace are also significant factors. In this context, the term “well-being at work” is becoming increasingly appearing and plays an important role especially in connection with aging employees. All these factors form the concept of work ability and were arranged in the so-called “Work Ability House”.
It is obvious that we consider age management in its general form to be a way of managing individual factors of working ability, which in this concept is formed by the so-called House of working ability. This includes health, competences, values, attitude motivations, working conditions and also the area of harmonizing family work life
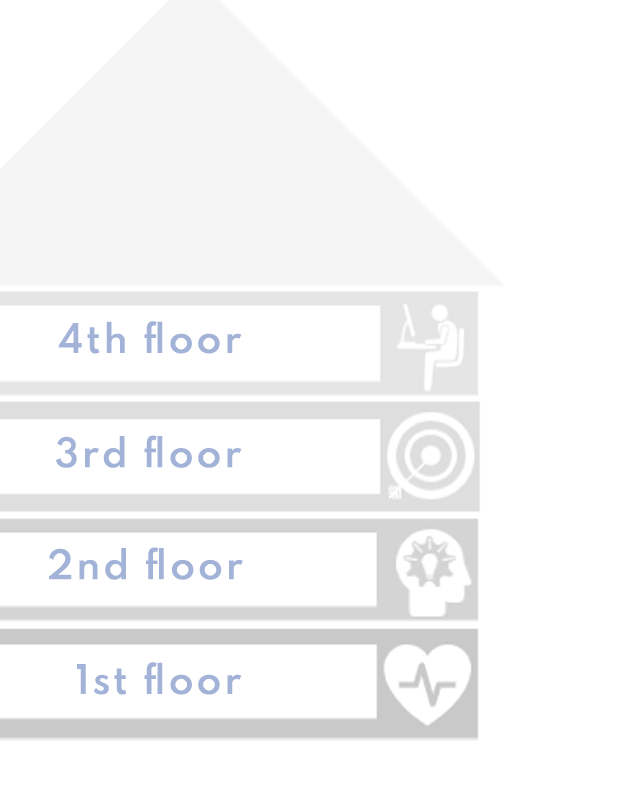
4th floor - workplace
- An open corporate culture and an appropriate leadership style based on respect for all generations,
- work ergonomics, workshops with physiotherapists (correct sitting posture, desk setup, work exercise, etc.),
- adapting and improving work organization (e.g. adapting production shift times to the sleep cycles, prevention of time stress and overwork),
- job rotation,
- workplace relaxation zones.
3rd floor - Motivation, values and attitudes
- Regular evaluations of employees with their superiors,
- regular surveys of employee satisfaction issues,
- work-life balance programs (flexible forms of work, shared workspaces, etc.),
- programs to support employees (e.g. in case of excessive stress – “the art of rest”, prevention of burnout syndrome, time management),
- support of work well-being (team building, workshops, ...),
- plans for employees returning to work after a long time (e.g. after maternity leave or long-term illness),
- aid for people with disabilities,
- company kindergartens.
2nd floor - Competences
- Trainee program,
- adaptation programs for new employees,
- regularly updated training plans,
- training planning considering the needs of different generations (aging workers – e.g. information technology and language courses),
- online or e-learning training attendance,
- intergenerational cooperation (diversity of teams), mentoring,
- career management and knowledge management.
1st floor - Health and functional capacity
- Healthy lifestyle and promotion of healthy eating,
- health “packages” – regular measurement of blood pressure, sugar level, BMI, vaccinations,
- employee health benefits (relaxation massages, expanded health care checks),
- rehabilitation and reconditioning programs,
- ban on smoking in the workplace (smoking cessation program or an employee obesity program).
How does work ability relate to your career?

Capacity, Employability and Work Ability
Basically three terms can be differentiated:
- The psychological, mental and physical capacity of a person are key to the fulfilment of work. The functional capacities describe person-related properties such as gender, constitution/fitness, health and age) and acquired knowledge, skills and abilities.
- Work ability describes the totality of factors that allow all people in a specific working situation to complete the tasks assigned to them successfully.
- Employability is a broader concept based on the essential possibility of employment. The concept of employability embraces the characteristics of a person with respect to the requirements and opportunities in the labour market.
Individual capacity
Individual capacity may be an intrinsic requirement in order to be able to carry out (work) tasks. However, work ability depends on the tasks to be carried out. Despite health limitations and poor qualifications, a person can still have stable work ability if the work requirements fit his or her capacities.
Work ability
Employability
However, employability represents a whole different dimension inasmuch as it considers the applicability of existing qualifications and capabilities in the labour market. The skills of a person are individual, while the operative conditions in which to be able to carry out work are largely left unconsidered.
In this respect, it is true to say that in order to increase employment levels for women and older people, the work ability approach is particularly relevant at a company level. At a macroeconomic level, employability also plays a role, especially with respect to general and vocational education.
Relationship between individual capacity/work ability and employability
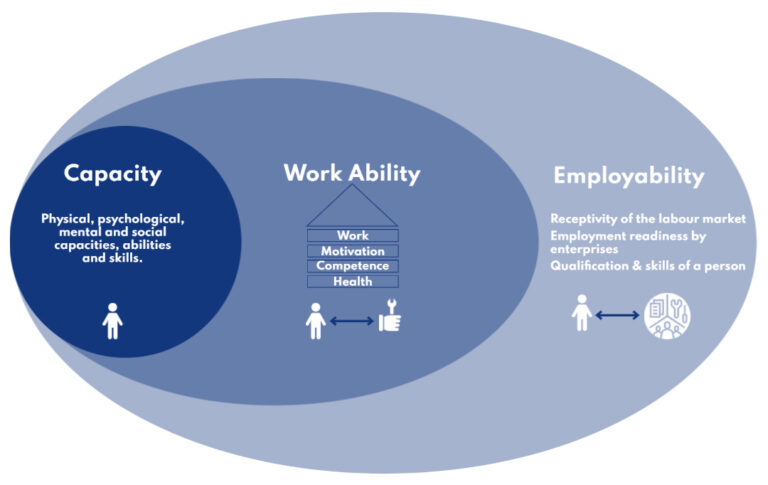
Source: based Kistler (2008) a Richenhagen (2009) own processing for the purposes of the WAM project.



